
After-sales service
Training
Contact Customer Service
0755-2357 0166
Pilot Training
Guizhou Dingfeng Technology Co., Ltd.
《Dingfeng Technology Civil Aviation License + Agriculture, Forestry and Plant Protection UAV Skill Training》
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to training institutions
2. Training objectives and targets
3. Training classes and qualifications
1. Multi-rotor drone class (class three, class four)
2. Training qualification
4. Training content
1. Theoretical course outline
2. Practical course outline
5. Examination rules and registration conditions
6. Training arrangements
1. Training start time and training cycle
2. Class time
3. Training costs
7. Answers to frequently asked questions about AOPA training and certification
1. Introduction to training institutions
Guizhou Dingfeng is one of the first domestic enterprises to obtain the training qualification of "Civil UAV Pilot Aircraft System Pilot Training Organization" approved by AOPA. The company integrates UAV R&D, production, sales, service, and training. It has rich practical application experience in the UAV industry and can provide students with practical application guidance. With a construction area of more than 1,000 square meters, there are professional training venues and airspace;

AOPA training qualification certificate

Q1 series multi-rotor drone plant protection machine
2. Training objectives and targets
Cultivate knowledge of aviation theory related to drones and practical operation skills of drones, obtain a drone cloud license issued by the Civil Aviation Administration of China after examination, and obtain both the Chinese Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association after applying for the dual certificates (AOPA) issued a unified national drone pilot and captain certificate.

The Civil Aviation Administration of China uniformly issues a sample of the drone cloud license certificate

China Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA) issued a uniform certificate sample
This training is for practitioners and job seekers in drone-related industries, university graduates and interns, vocational and junior college graduates and interns; secondary vocational and technical secondary school graduates and post interns, drone enthusiasts, etc. UAV-related professional students, practitioners and enthusiasts conduct enrollment training.
3. Training classes and qualifications
1. Multi-rotor drone class (class three, class four)
Multi-rotor UAV has small size, light weight, low noise and good concealment. It is suitable for multi-platform and multi-space use; it can take off and land vertically without a catapult or launcher for launching. It can hover, fly sideways, and reverse. Fly; Low flying height, strong maneuverability, strong ability to perform special tasks; simple structure, flexible control, low cost, small propeller, good safety, convenient disassembly, and easy maintenance. It is widely used in education and scientific research. , Aerial photography, military, police security, agriculture and other fields.
2. Training qualification
There are also three types of UAV driving licenses: pilot license (driver within visual range), captain's license (over-visual range pilot), and instructor license.
1. The driver, also known as the line-of-sight driver, refers to controlling the drone within the visual range of the naked eye.
2. The captain, also known as the over-the-horizon pilot, means that the drone can be operated outside the visible range of the naked eye.
3. The instructor is one level higher than the captain and can train the qualifications of the pilot and captain.
4. The difference between the captain and the pilot is that the pilot only needs to master the GPS mode to fly. The captain also has to learn to fly in the attitude mode, and one more ground station setting is required, which requires high flight skills. UAV instructors are mainly training teaching methods, focusing on practical teaching applications in the future.
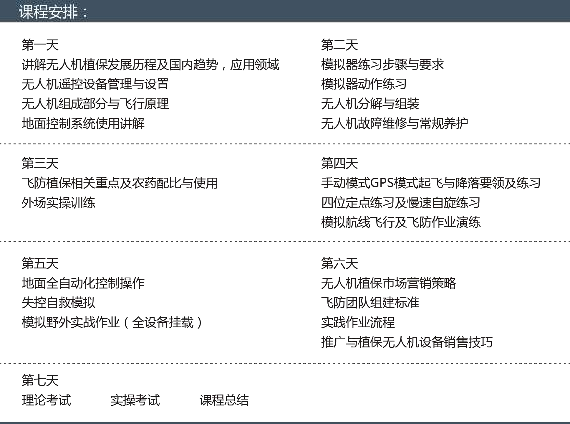
4. Training content
1. Theoretical course outline
| Course | Training content | Class |
| 1 | UAV overview and system composition | 8 class hours |
| 2 | Civil Aviation Regulations and Terminology | 3 class hours |
| 3 | Airspace flight and declaration | 7 class hours |
| 4 | Aviation Meteorology and Flight Environment | 6 class hours |
| 5 | UAV classification and mainstream layout form | 5 class hours |
| 6 | UAV structure | 4 class hours |
| 7 | Flight principle and performance | 6 class hours |
| 8 | Communication link and mission planning | 5 class hours |
| 9 | UAV system characteristics used | 10 class hours |
| 10 | Drone flight manual and other documents | 6 class hours |
| Theory course total hours | 60 hours | |
2. Practical course outline
| Course | Subject | Ground | Take flight | Solo | Total time |
| 1 | Flight simulation | 8 | 8 | ||
| 2 | Aircraft disassembly, maintenance, repair and maintenance | 10 | 10 | ||
| 3 | Ground station setup and pre-flight preparation | 8 | 8 | ||
| 4 | Take-off and landing training | 4 | 8 | 12 | |
| 5 | Take flight | 6 | 6 | ||
| 6 | Solo | 10 | 10 | ||
| 7 | Manipulation and command in emergency | 6 | 8 | 14 | |
| 8 | Assessment and graduation | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Total | 28 | 18 | 28 | 74 | |
5. Examination rules and registration conditions
1. Exam rules
1) Driver within the line of sight (former driver): Pass the theory 70 points, practical test items: In GPS mode, fly level 360° spin, level character, oral test.
2) Over-the-horizon pilot (former captain): Passed theoretically 80 points; practical test items: in stabilization mode, flying horizontal 360° spin, horizontal character, oral test, ground station.
3) Requirements for field practice exams:
Take-off and landing, tail-to-tail hover, 4-position hover, slow spin, horizontal horoscope.

2. Registration conditions
1. At least 16 years old, with a junior high school education level or above.
2. Abide by laws and regulations, have no bad behavior, and have no criminal record within three years (provide relevant certificates).
3. Physical requirements: corrected visual acuity above 1.0, no color blindness, color weakness, no infectious diseases, no cardiovascular and cerebrovascular and mental diseases, no physical disabilities, no bad habits.
※ Please note! In any of the following situations, you are not allowed to apply for a driver's certificate:
Have quality heart disease, epilepsy, Meniere's disease, vertigo, hysteria, tremor paralysis, mental illness, dementia, and neurological diseases that affect the movement of limbs and other diseases that hinder safe flight;
Those who have been addicted to taking drugs, injecting drugs, or long-term use of dependent psychotropic drugs have not been quit.
6. Training arrangements
1. Training start time and training cycle
Classes are opened every month, as you go to school, weekend classes, off-duty classes...you can choose
Training time for no-foundation trainees (28 days)
Training time for basic trainees (15 days)
2. Class time
9:00-12:00 am (2 hours lunch break) 14:00-17:00 pm
3. Training costs
1. The original application form. Note: The filling in the "application form" must be clear and complete.
2. The original and one copy of the ID card.
3. Two one-inch white background photos and an electronic file of white background photos.
4. Registration process: Submit the registration form to the enrollment teacher-pay the training fee before the start of the class-go through the enrollment procedures at the training base-receive the teaching materials in the training classroom with the student card-the training teacher arranges the class-report on the 12th of each month Examination plan-take the theory test on the 19th of each month-take the practical examination on the 20th of each month-finish-issue the certificate.
7. Answers to frequently asked questions about AOPA training and certification
1. Why should I get a drone pilot certificate from the Civil Aviation Administration?
In September 2016, the Civil Aviation Administration of China issued the new "Civil Unmanned Aircraft System Air Traffic Management Measures", and in July 2016 issued an advisory notice "Civil Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Pilot Management Regulations", which stipulated that civilian drone pilots Management methods and procedures. At present, there is no control over the purchase of drones, leading to undocumented "black flying" from time to time. Due to the lack of professional training, drone pilots do not understand the corresponding aviation regulations when flying. I don’t know very much about what circumstances and where to fly. There are a lot of safety accidents and there are increasing risks to society. The new management measures compulsorily stipulate that drone pilots must hold a qualified driving license. The domestic control of black flight will become stricter, and driving without a license will face more and more stringent penalties. Therefore, for those who own drones, the risk of black flying will become greater and greater, and the black flying of drones will face legal and property risks similar to those of driving a car. So if you want to avoid this kind of risk, you have to obtain a "drone pilot certificate."
Secondly, UAV applications have developed rapidly in recent years, and UAVs have been seen everywhere in the fields of aerial photography, plant protection, line inspection, and monitoring. Market demand is growing explosively. my country’s current demand for drone pilots is very large, including plant protection, surveying and mapping, electricity, meteorology, environmental protection, land, maritime surveillance, and other industry-level drone pilots. The demand is about 100,000, and the demand is year by year rise rapidly. As of the end of 2016, there are only more than 10,000 licensed pilots in my country, and they will be in a state of short supply for a long time in the future. Taking the UAV driver's license from the Civil Aviation Administration of China means employment is guaranteed.
What driver's license test?
According to the “Regulations on the Management of Civil UAV Pilots (AC-61-FS-2016-20R1)” issued by the Flight Standards Department of the Civil Aviation Administration of China in July 2016, the certification of civil UAV pilots is still divided into
There are 3 categories: pilot, captain, and instructor. These three types of certificates can be divided into a variety of certificates according to the category level (such as: fixed wing, multi-rotor) and level level (level level is divided by the weight of the drone).
The main courses of the Civil Aviation Administration of UAV certification are as follows:
1. What is a multi-rotor drone?
An aircraft with three or more rotors.
2. What are the advantages of the rotorcraft?
Advantages of multi-rotor drones: (1) Small size, light weight, low noise, good concealment, suitable for multi-platform and multi-space use; (2) It can take off and land vertically without a catapult or launcher for launch; 3) Low flying height, strong maneuverability, and strong ability to perform special tasks; (4) Simple structure, flexible control, low cost, small propeller, good safety, convenient disassembly, and easy maintenance.
3. Application fields of multi-rotor:
Urban management, agriculture, geology, meteorology, electric power, electric power inspection, rescue and disaster relief, video shooting and other industries.
4. What is a basic class?
A basic class means that students have a certain degree of experience in operating drones (only flying through the DJI Wizard, Wu, and Yu series are not considered experience), and the technology is relatively good, and they can be considered as basic students if they can pass the professional instructor test.
9. What is the difference between Type Ⅲ and Type Ⅳ and Ⅴ?
Category Ⅲ refers to drones that can operate under 25kg; category Ⅳ refers to drones that can operate under 150kg; and category Ⅴ refers to certificates for operating plant protection aircraft.
10. What is the difference between a captain and a pilot?
The pilot can only operate the UAV within the visual range; the captain can operate the UAV beyond the visual distance, and can use the ground station to operate the UAV, which has wider authority.
11. What are the subjects for the pilot and captain certificate test? Pilot: theory, comprehensive question and answer, practical operation;
Captain: theory, comprehensive question and answer, practical operation, ground station;
1. UAV Agriculture, Forestry and Plant Protection Application Course



 粤公网安备 44030602004835号
粤公网安备 44030602004835号